
At the heart of Demographic Winter lies the Sexual Revolution – which is usually traced to the 1960s but whose origins lie decades earlier. This sea-change in attitudes and behaviors included first separating sex from childbearing, then from marriage, and finally from love or any sense of commitment. Pornography, premarital sex, promiscuity and perversion were all normalized. Abortion was legalized and, in developed nations, enshrined as a basic human right. Because of the Sexual Revolution’s efforts, not only have individual attitudes toward having children, but also the entire world’s attitude. The plummeting birthrates around the globe are almost sure to bring declining populations, massive economic disruptions, and all the problems stemming from under-population.
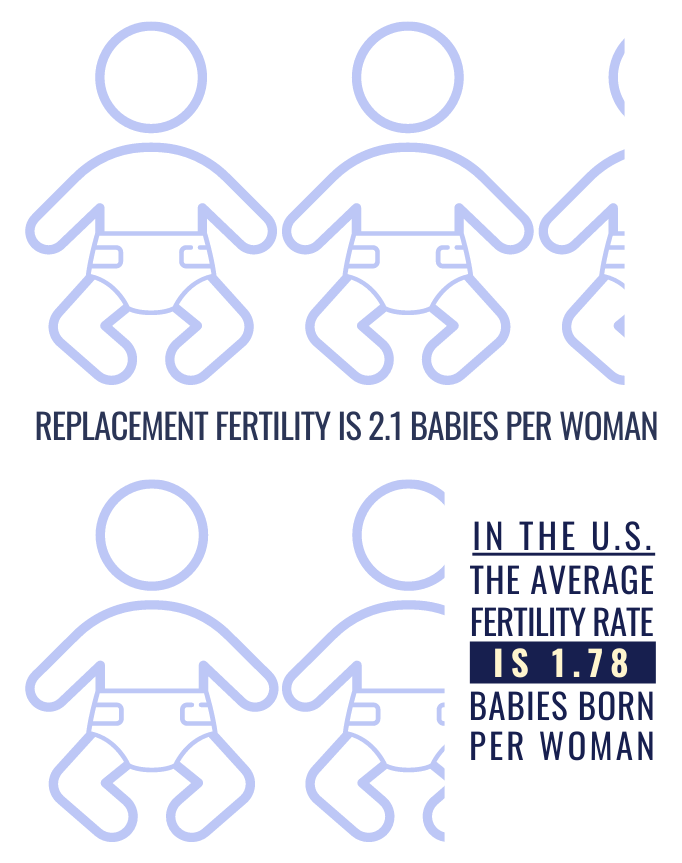
A nation's fertility rate is the number of children the average woman has in her lifetime. A fertility rate of 2.1 is needed to replace the current population. A higher rate, and the population will increase, a lower rate, and it will decline.
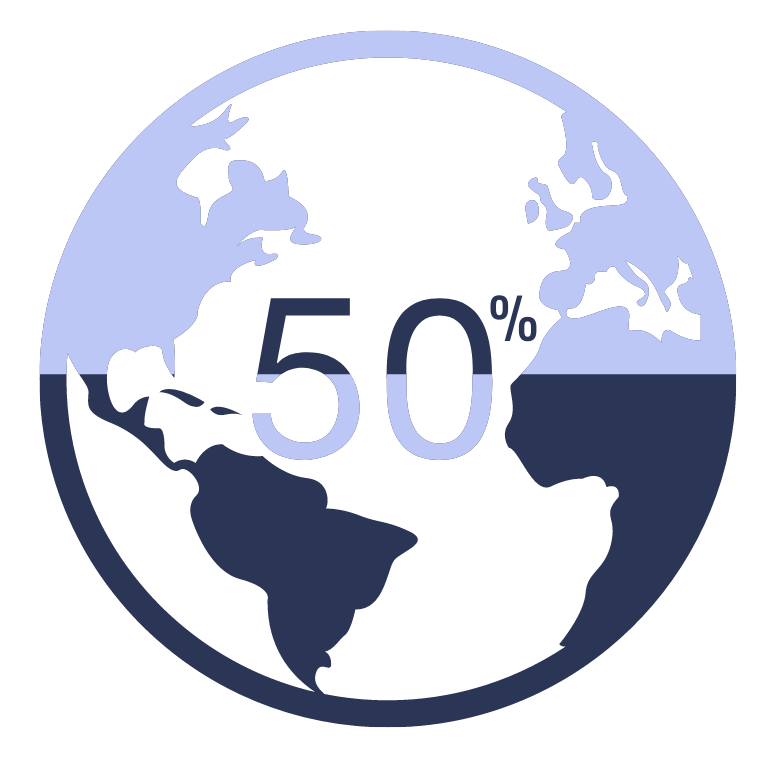

Worldwide, fertility has declined dramatically in the past 70 years. In 1950, worldwide, the average woman had 4.7 children. By 2017, that figure was cut almost in half, falling to 2.4. Half of all countries now have below-replacement fertility. Global fertility rate is expected to fall to 1.9 births per woman by 2100 and global population decline could begin as early as 2064.
Africa is the only continent expected to experience strong population growth for the rest of the century. Between 2020 and 2100, 90 countries are expected to lose population, including two-thirds of all countries in Europe. In Latin American and the Caribbean, half of the region’s 50 countries are expected to lose people.

For the European Union as a whole, the total fertility rate is 1.53. For countries like Italy, Greece and Spain, it’s considerably lower. All other things being equal, countries with a TFR of 1.3 or lower will lose half their population every 45 years.

In 2018, the U.S. birthrate fell for the 4th. consecutive year. The number of babies born fell by 2%. According to the Census Bureau, in 1950, the average American woman had 3.5 children. Today, that number is below 2. Today, 47.8 million Americans are over 65. By 2050, that’s projected to rise to 83.7 million.

Japan’s total fertility rate is 1.4, roughly 33% below replacement. Between 1989 and today, its over-65 population more than doubled - from going 11.4% of the total population to 28.4% in 2020. Between 2015 and 2020, Japan’s total population declined by more than 868,000. So many Japanese are dying alone at home, because they have no one to care for them (no children or grandchildren) that an industry has sprung up devoted to disposing of their remains. The Japanese even have a name for the phenomenon: Kodokushi - “lonely death.”
Japan’s population is expected to decline by another 27 million by 2053. Japan has the oldest population of any developed nation. Its over-65 population is expected to go from 26.6% of total population in 2015 to 38.4% by 2065. Each year, more adult diapers than baby diapers are sold. Social security expenditures account for 34.2% of spending. There are 200 to 300 hamlets where 100% of the population is over 75.
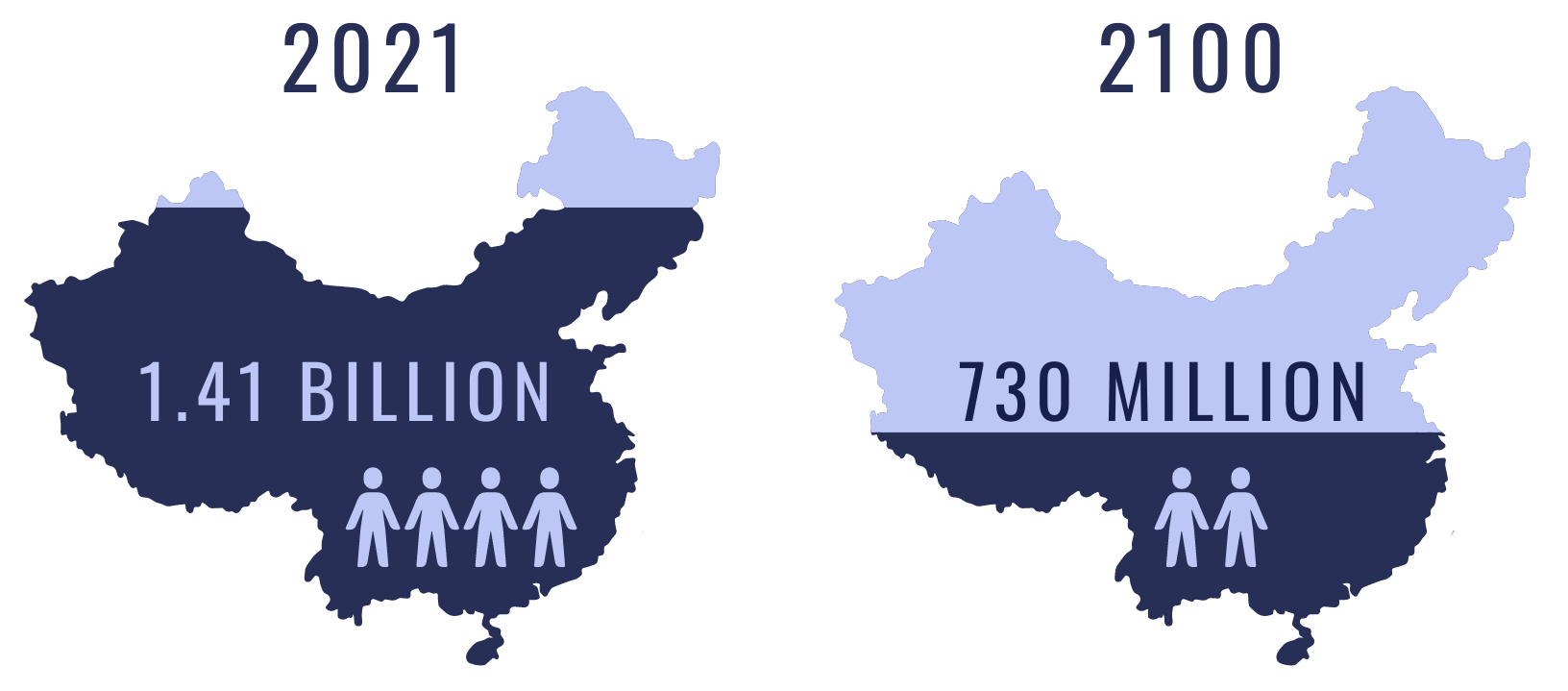
Due to its one-child policy (in place for 44 years) China’s population is expected to fall from 1.41 billion today to 730 million by the end of the century. China would then have as many 85-year-olds as 18-year-olds.

For the first time in history, just under half the world’s population (48%) of child-bearing age uses some form of birth control. The global contraceptive market will generate an estimated $43.8 billion in 2022 (more than double the total in 2015). In most cases, this is financed by governments or employers.

In 2020, Italy’s birth rate was the lowest since unification in 1861. Its population fell by over 384,000 – the equal to the population of Florence.

In 2018, Russian births fell to 1.69 million, the lowest in a decade. The government announced plans to spend $8.6 billion over three years to encourage Russians to have more children, including mortgage subsidies and payments to new and growing families. In 2017, Russia’s population declined by 134,400.

Spain has a fertility rate of 1.33. If current trends continue, each new generation will be 40% smaller than the last. In 2015, Spain had 1,500 abandoned villages, due to declining population.

Worldwide, there are over 73 million abortions per year. That's more than three times the number of military death in World War II, the bloodiest conflict in history. But with abortion, instead of soldiers dying in battle, these fatalities are self inflicted by each nation.
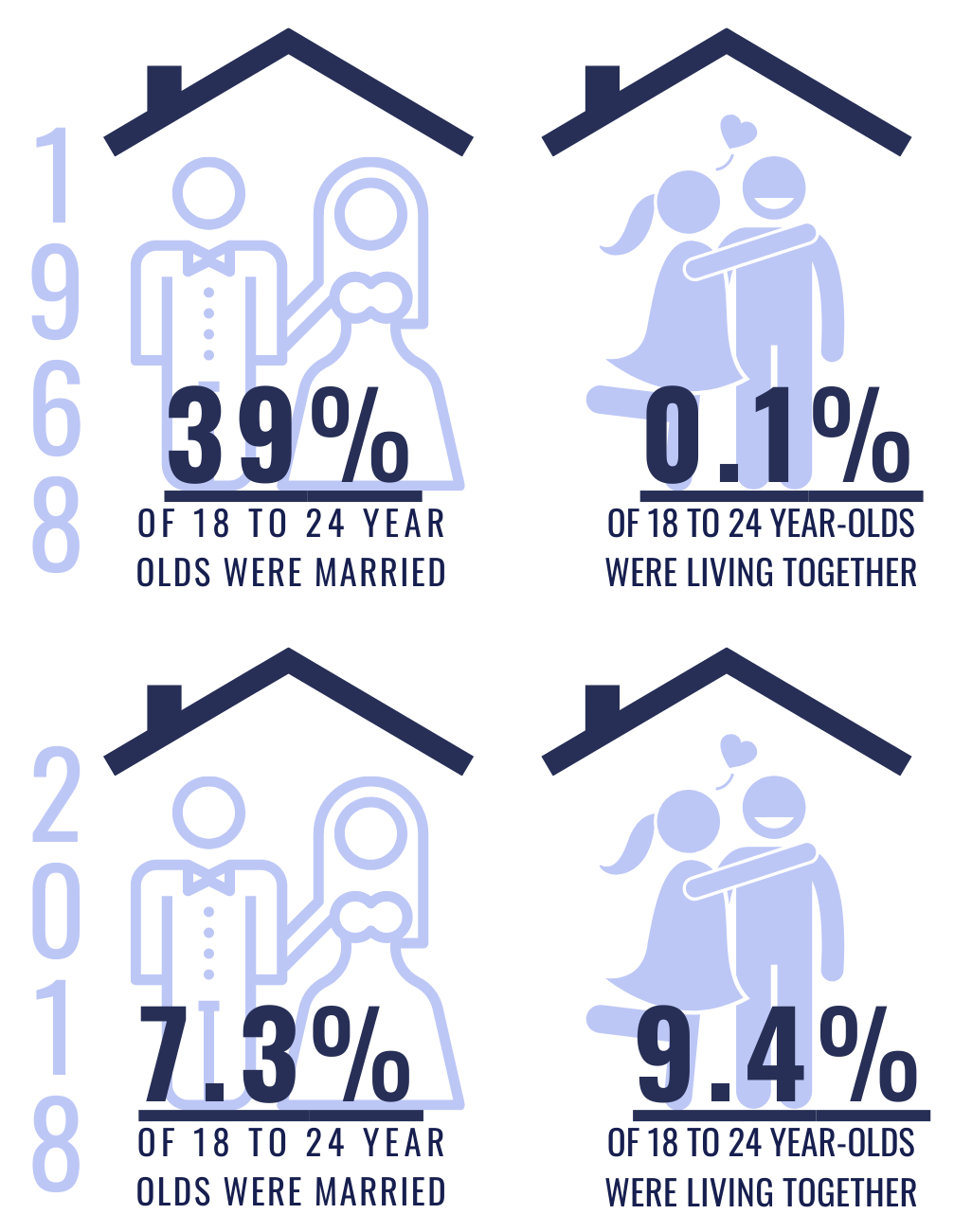
Given the impermanence of these relationships (half last no more than 18 months), cohabitating couples are more likely to be childless or to have fewer children then their married counterparts.
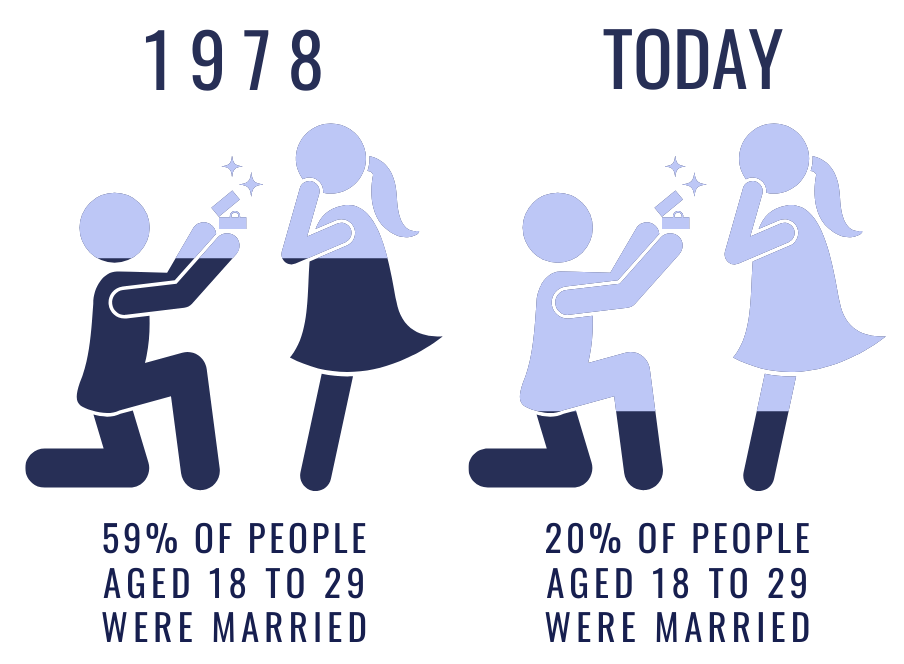
Among 18-34 year olds (those in their prime childbearing years), 59% were married in 1978. By 2018, that number had fallen to 20%. Inevitably, fewer marriages means fewer children.
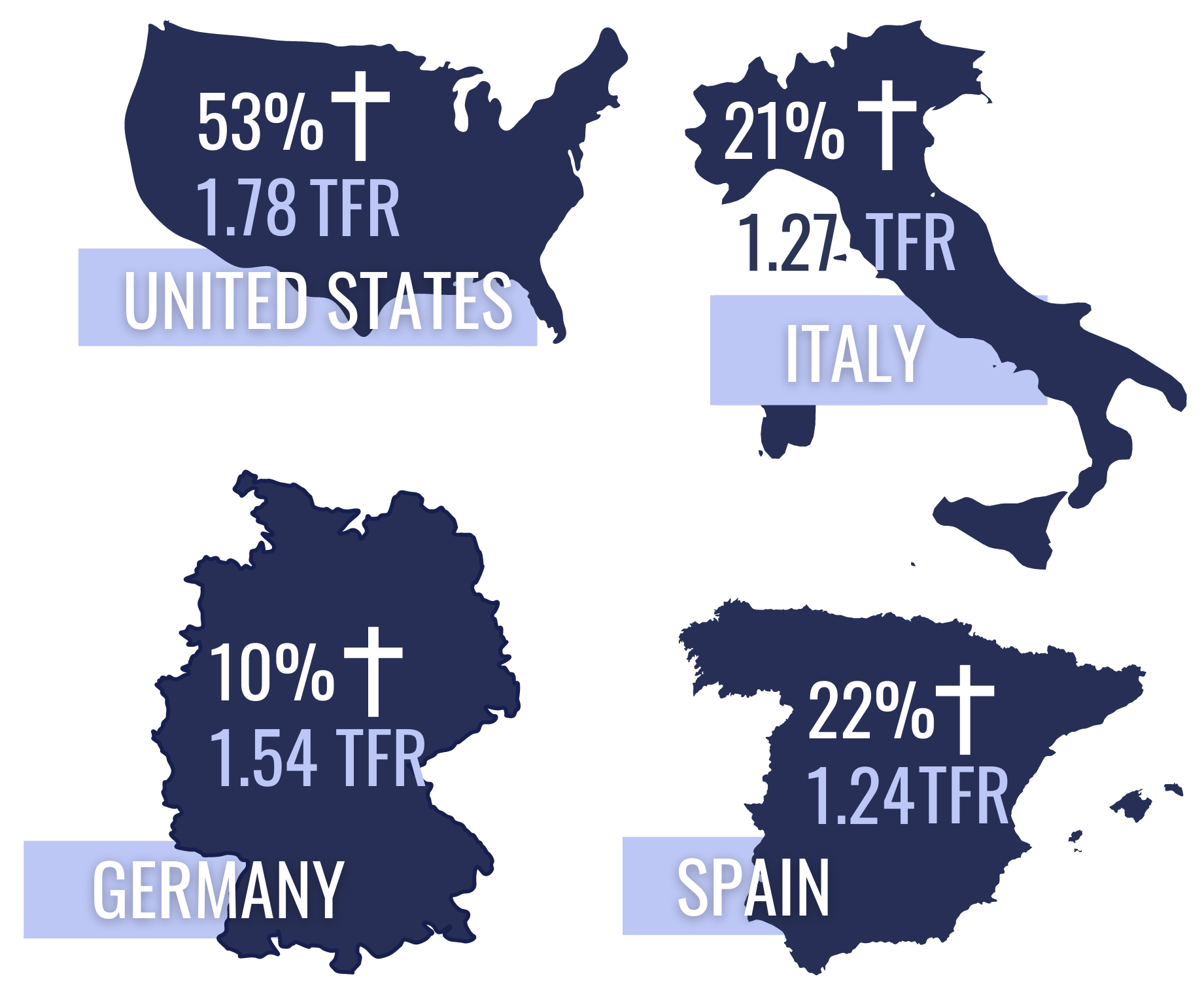
There is a direct correlation between faith and fertility. In a 2017 survey, 53% of Americans said religion was very important to them, compared to 11% in France, 10% in Germany, 22% in Spain, and 21% in Italy. Consequently, for the European Union, the fertility rate (TFR) is 1.53 compared to 1.78 in the U.S.
The Ruth Institute is a 501c3 non-profit organization.
630 W. Prien Lake Road, Suite B #246, Lake Charles, LA 70601
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |